In 1912, a remarkable discovery sent shockwaves through the town of Delavan, Wisconsin. It was a discovery so astonishing that it would challenge conventional ideas about human history and prehistoric beings. This remarkable find involved the unearthing of gigantic human skeletons, shedding light on a chapter of the past that defied explanation.
While excavating a burial mound near Delavan Lake, workers unearthed several ancient burial sites, each containing an abnormally large human skeleton. These skeletons measured between 7 to 9 feet in length, significantly larger than the average human. The discovery immediately captured the imagination of both locals and researchers alike.

Researchers and archaeologists descended upon Delavan to examine the findings. The giant skeletons were carefully measured, pH๏τographed, and documented. The remains were well-preserved, and the bones appeared anatomically similar to those of a human, except for their extraordinary size.
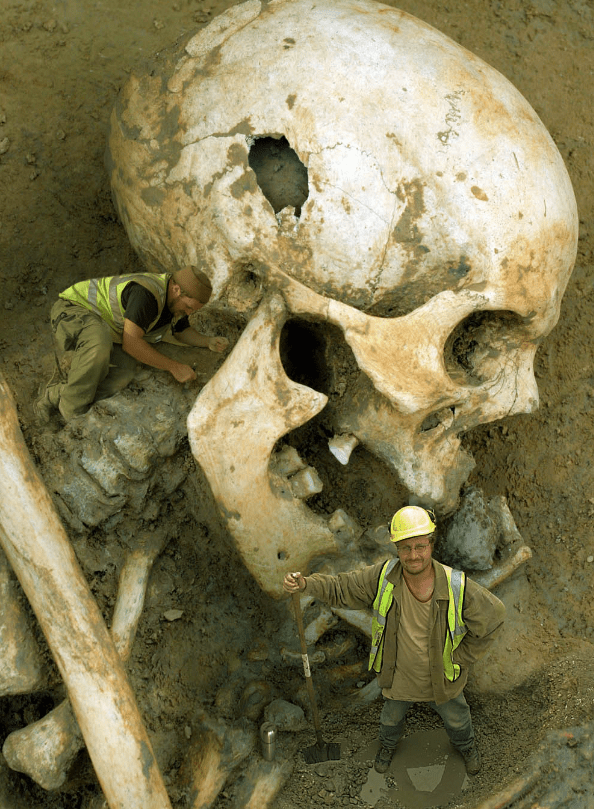
The discovery sparked numerous theories and debates about the origin of these giants. Some speculated that these beings might have been an unknown human-like species that roamed the Earth in prehistoric times. Others suggested that the skeletons could be the result of a rare genetic condition that caused abnormal growth. However, no definitive conclusion was reached, and the mystery of the Delavan giants remained unsolved.
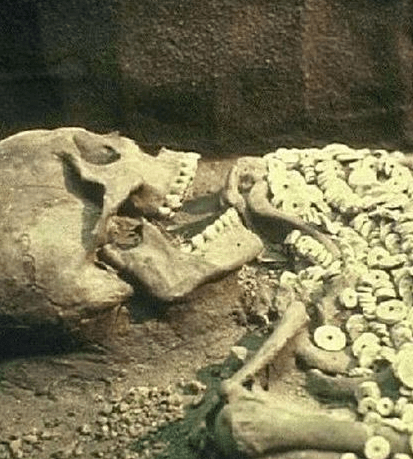

Unfortunately, as time pᴀssed, the giant skeletons began to vanish, leaving behind only pH๏τographs and anecdotal evidence. Many speculate that the remains were either lost, destroyed, or kept hidden, perhaps due to the controversial nature of the discovery.
The astonishing Delavan findings serve as a testament to the intriguing and enigmatic aspects of history that continue to captivate our imagination. Whether they were remnants of an unknown ancient civilization, unusually large individuals, or an entirely different species, the giant skeletons of Delavan remain a fascinating and perplexing chapter in the world of archaeology and anthropology.